
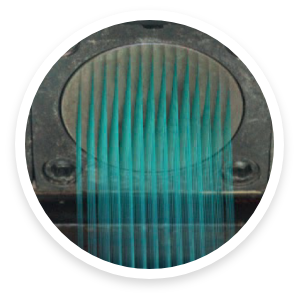

why solution-dyed olefin?
OLEFIN is a manmade fiber that is typically used along with other fibers to create outdoor fabric blends. It is often used in outdoor furniture and for a variety of other applications, including house wrap, marine coverings, and clothing. Depending on its chemical structure, olefin may also be referred to as polyethylene or polypropylene. It is manufactured similarly to polyester and nylon. Olefin typically has a smooth texture. It is a durable fabric that dries quickly and is resistant to weathering, chemicals, and stains.
usage areas
of olefin
OLEFIN fabrics are versatile for a variety of applications. They are used in automotive interiors; home furnishings such as patio cushions, flooring, and wall coverings; and industrial uses such as disposable nonwovens, filter fabrics, bags, and geotextiles.
toSUN branded solution-dyed Olefin outdoor fabrics offered by TOSUNOGLU, go through the same process as solution-dyed acrylic products to obtain their color and strength. Olefin provides all the necessary performance that is expected from an outdoor fabric.